
Digital skills
Digital literacies are the capabilities which fit someone for living, learning, working, participating and thriving in a digital society.
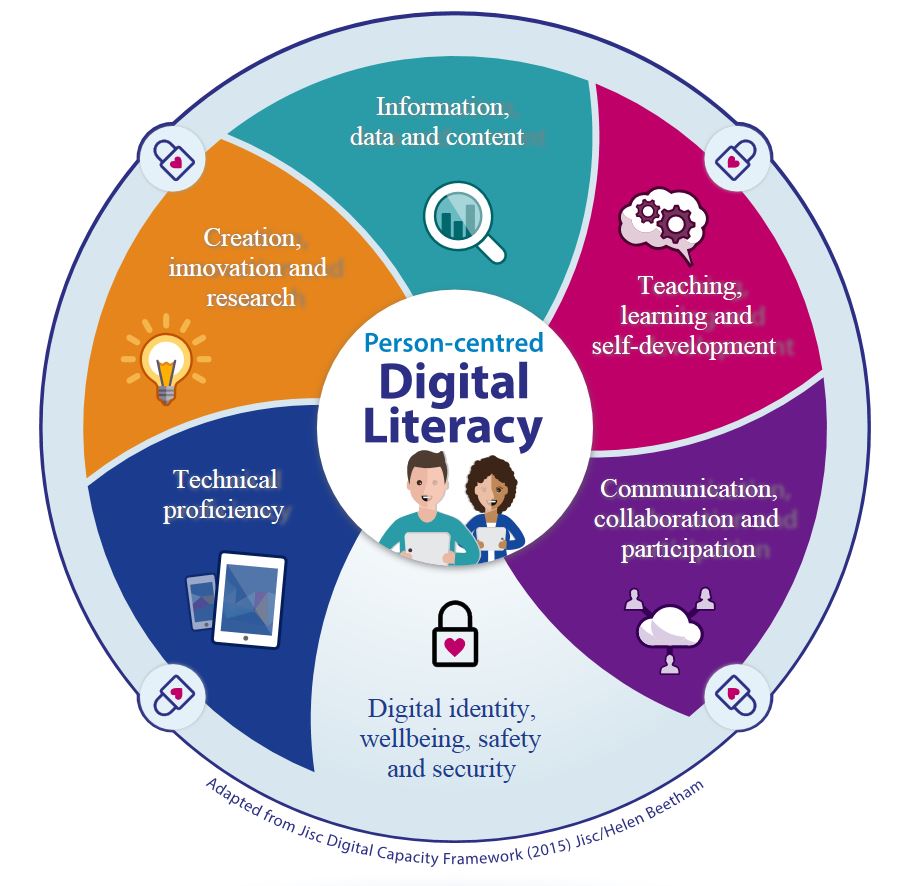
Becoming a digitally-literate person involves developing those skills, attitudes, values and behaviours that can be categorised under the following headings:
- digital identity, well-being and safety
- communication, collaboration and participation
- teaching, learning and self-development
- technical proficiency
- information, data and media literacies
- digital creation, innovation and scholarship.
Being digitally literate across a range of domains to proficient levels helps us more easily acquire other skills and competencies in life. See: Improving digital literacy, (Health Education England and RCN (2017).
The areas covered by the framework form a whole, where each area is of equal importance. Technical proficiency or expertise is one area, among the six covered by the framework. The framework should be of use to all students, nurses, midwives and health care support workers throughout the UK.
Health Education England has produced a further publication to help individuals identify and develop their digital capabilities. See: A Health and Care Digital Capabilities Framework (2017).
The six domains and the nursing context
Examples of skills, attitudes, values and behaviours
Digital identity, well-being and safety: Managing personal and professional identities – digital footprint – recognizing online bullying – managing time online effectively
Information, data and media literacies: Support citizens + patients find reliable information – help them use Electronic Patient Health Records and portals – using technology to co-ordinate care – identify information needed to improve clinical decision making – understanding how data is structured within health record systems – complying with legal, professional requirements when using and sharing information
Teaching, learning and self-development: Participating in learning using digital media such as online learning and social networking – using digital tools to plan and reflect on learning – understanding professional behaviours in social media spaces
Communication, collaboration and participation: Using appropriate forms of communication – acknowledging points of view and cultural differences – online therapeutic relationships – developing professional networks
Technical proficiency: Using devices, applications and software for a range of nursing tasks – stay up-to-date with evolving technology – ability to provide feedback on technology – articulating benefits and risks
Digital creation, innovation and scholarship: Ability to work with patients + citizens to co-design and co-develop digitally enabled ways of working – shaping research agenda for digital innovation
Page last updated - 14/12/2023







